An Overview of Colorectal Cancer Screening Tests
March is National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, an important time to spread awareness and learn more about the risks associated with colorectal cancer.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer and the second-leading cause of cancer deaths in the world. In the United States this year, an estimated 151,030 adults will be diagnosed with colorectal cancer and an estimated 52,580 will die from the disease.
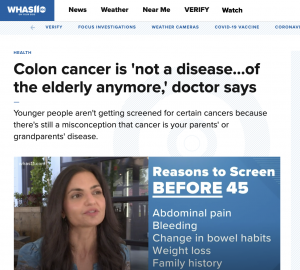
Despite its significant rate of incidence, colorectal cancer is highly preventable through the use of screening tests. Gastroenterology Health Partners, in conjunction with the American Cancer Society and Digestive Health Partners Association, recommends that those with an average risk start screenings at age 45.
Of the colorectal cancer screening tests that we offer, colonoscopy remains the gold-standard of effectiveness and is strongly suggested for anyone eligible. Observational studies have suggested that colonoscopy can reduce colorectal cancer occurrence by 40% and mortality rates by 60%.
If you’re considering scheduling a screening test, talk to an experienced gastroenterologist. They can help you make the right decision for your needs.
Keep reading to learn about six commonly-offered colorectal cancer screening tests.
6 Common Colorectal Cancer Screening Tests
1. Colonoscopy
As mentioned above, the colonoscopy is the best diagnostic tool available. This out-patient procedure involves the use of a thin, flexible tube with a camera to exam the lining of the colon (large intestine) for abnormalities such as polyps. Some polyps can be removed with a scope during the procedure. Your doctor may also take tissue samples for analysis as well.
While the colonoscopy does require prep and recovery time, it is a fast, virtually risk-free procedure. Afterwards, your doctor will discuss your results with you and recommend whether you should be screened in 1, 5, or 10 years. To learn more about the colonoscopy, how it works, how to prepare, and more, read here.
2. Fecal immunochemical test (FIT)
Often considered the second choice after a colonoscopy, the fecal immunochemical test (FIT) offers a non-invasive method for identifying colorectal cancer. The test, often performed at home, tests for hidden (occult) blood in the stool. This unnoticeable blood is often an early-sign of colorectal cancer.
If you test positive for hidden blood during a FIT test, your doctor will want to perform another test, most likely a colonoscopy. FIT, unlike colonoscopy, is unable to actually identify or remove polyps and abnormal tissue. Therefore, the FIT is not really a viable “preventative” test and has a much lower accuracy rate.
3. CT Colonography
The CT Colonography is also known as a “virtual colonoscopy.” This test uses a CT scan (a form of x-ray technology) to exam the colon for polyps. A small scope is inserted slightly into the colon to inflate it with air. Then, pictures are taken of the entire colon. The CT Colonography is highly effective, and, unlike a colonoscopy, it doesn’t require sedation. However, unlike a colonoscopy, this exam doesn’t actually remove precancerous polyps, it only can identify them.
4. Cologuard
Cologuard is another non-invasive, at-home colon screening test. Much like the FIT test, it looks at stool DNA samples. While Cologuard is generally more effective than FIT, it still doesn’t compare to the effectiveness of the colonoscopy–while colonoscopy is known to identify over 70% of precancerous polyps, Cologuard only identifies around 42%.
5. Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
A flexible sigmoidoscopy is a comparable procedure to the colonoscopy. It is an exam of the lower part of the colon using a small, flexible, lighted tube. The tube, called a flexible sigmoidoscope, has a camera which allows the doctor to view the inside of the rectum and the sigmoid colon—about the last two feet of the large intestine. Unlike a colonoscopy, this procedure does not allow the doctor to see the entire colon; any cancers or polyps far in the colon cannot be detected.
6. Capsule Endoscopy
A capsule endoscopy is a procedure that examines the lining of the middle part of the small intestine, the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. This procedure is necessary because a standard endoscope or colonoscope cannot reach this part of the bowel. Capsule endoscopy is often used to search for causes of bleeding as well as detect polyps, tumors, ulcers, and IBD.
During this procedure, the patient will swallow a tiny pill containing a video camera, light source, and battery. The camera will take 2-3 pictures per second for up to 12 hours, traveling through the GI tract. The photos are saved automatically to a recording device and strung into a video.
While capsule endoscopy is effective for detecting and documenting significant lesions attributed to conditions such as IBD, tumors, and ulcers, it is significantly less effective as a colon screening test compared to colonoscopy.
When it comes to colon cancer screenings, the experienced medical team at Gastroenterology Health Partners is here to serve you. To learn more about our services or to schedule an appointment at one of our offices in Southern Indiana or Kentucky, contact a Gastroenterology Health Partners location near you.